Decision list
Decision lists are a representation for Boolean functions[1]. Single term decision lists are more expressive than disjunctions and conjunctions, however 1-term decision lists are less expressive than the general disjunctive normal form and the conjunctive normal form.
The language specified by a k-length decision list includes as a subset the language specified by a k-depth decision tree.
Learning decision lists can be used for attribute efficient learning[2].
Definition
A decision list (DL) of length 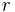 is of the form:
is of the form:
ifthen output
else if
then output
... else if
then output
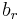
where 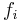 is the
is the 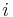 th formula and
th formula and 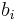 is the
is the 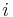 th boolean for
th boolean for 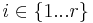 . The last if-then-else is the default case, which means formula
. The last if-then-else is the default case, which means formula 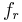 is always equal to true. A
is always equal to true. A 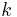 -DL is a decision list where all of formulas have at most
-DL is a decision list where all of formulas have at most 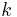 terms. Sometimes "decision list" is used to refer to a 1-DL, where all of the formulas are either a variable or its negation.
terms. Sometimes "decision list" is used to refer to a 1-DL, where all of the formulas are either a variable or its negation.